Listen to the article – Critical Crossroads for EU Foreign Policy Amid Upcoming Elections and Public Dissent
Decisions That Define a Generation
Europe finds itself at a critical juncture, facing challenges that threaten its position in the global arena. The Union has faced significant challenges stemming from cultural, social, and political differences among its member-states, amid the economic repercussions that EU is currently struggling with since the pandemic and particularly since the outbreak of the hostilities in its neighborhood.[1]
These divisions have strained EU unity, leading to increased polarization and discord. The Russian war in Ukraine and the Israel-Palestine conflict have exacerbated these tensions, placing additional financial burdens on the EU amid the widespread refugee flows and suffering.[2] Moreover, these conflicts have contributed to the growing trend of militarization, nuclear proliferation, and armament in Europe. For instance, EU’s largest economy, Germany, is currently experiencing a severe economic and industrial decline. The collapse is attributed to three main factors: sky-high energy prices, reduced exports to China, and increased military expenditures, coupled-up with the external pressure of major actors to disrupt relations with Russia and China.[3] Against this backdrop, the forthcoming 2024 EU elections carry profound significance, resonating across the European Union with heightened public interest. Central to this discourse are the ongoing conflicts in Ukraine and the Middle East, which will demand critical attention and decisive action from the successor EU parliament.
How can we help?
Intelligence Solutions
The combination of business, market and strategic intelligence ensures result-driven outcomes for our customers.
Risk management
Risk management through the responsibility of taking risk ownership while ensuring safety and security
Strategic Advisory
The first step in protecting your organization, assets and people is the identification of the risks and threats.
As the second-largest democratic exercise globally, the June election will shape the trajectory of European politics for the next five years. With 720 parliamentarians set to be elected by a populace of 450 million, the outcome will influence critical decisions spanning digital privacy, international trade, climate action and security.
The election outcome will also serve as a barometer for Europe’s political direction, amidst a global trend towards rightward shifts. While various ideological factions, including liberals, socialists, and populist right-wing parties, vie for representation in the EU parliament, forecasts suggest significant gains for right-wing factions.
However, an outright victory for far-right politics appears improbable due to the diverse political landscape within the EU. (Fig.1) Nonetheless, the increased presence of such parties foreshadows perpetuation of EU’s internal divisions and heightened social polarization, impacting EU’s foreign policy discourse. The confluence of these factors, compounded by the socio-economic repercussions of the pandemic, exacerbates social discontent, and far-right parties exploit these sentiments, further hinting of deepening divisions and impeding the EU’s decision-making processes. The raging wars in Eastern Europe and the Middle East are just another factor which has a significant impact on European society, economy and security, which bear the potential to divert the current political discourse of the Union.
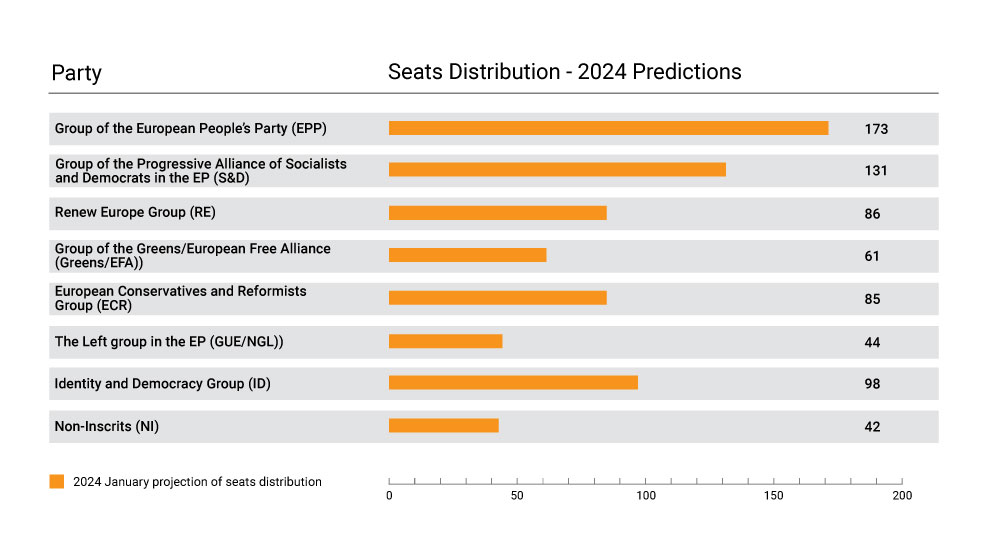
Fig.1 European Parliament Seats Distribution | Forecast January 2024
The purpose of the analysis is to inform investors about the current EU foreign policy discourse and societal discontent across EU, particularly in relation to the wars in Ukraine and Gaza, and in light of the upcoming EU elections. The insights would help investors steer the evolving political and economic landscape in the EU effectively. Considering the current EU foreign policy discourse, the escalating geopolitical tensions, the analysis argues that the societal discontent will likely escalate should the incoming EU parliament remains on the same foreign policy course. The analysis also highlights the dangers of “spiling-over” of hostilities on EU territory, as it would further negatively impact the economic prospects of the Union and deteriorate its role as a competitive economic power in general.
01
Current EU Strategies in Crisis Zones
01
Current EU Strategies in Crisis Zones
The ongoing conflicts in Ukraine and Israel significantly strained EU’s economic performance by disrupting energy supplies, inflating costs, destabilizing trade routes, and reducing market confidence, which collectively impeded EU’s economic growth and stability. In addition, EU’s divergent approaches to supporting Ukraine’s territorial integrity and addressing the Palestine-Israel conflict reflect contradictory policies that triggered social discontent, skepticism and controversy among EU citizens regarding their efficacy and ethical implications. Such dual approach led to further deepening the internal divisions within the Union.
Regarding Ukraine, the EU has maintained a commitment to supporting its territorial integrity, albeit with nuanced approaches across member-states. In fact, during the last two years, EU has implemented a series of comprehensive policies aimed at supporting Ukraine in the face of ongoing conflict with Russia. These policies encompass various areas such as political, economic, military and humanitarian assistance. Key initiatives include the establishment of the Ukraine Facility,[4] offering up to USD 54.21 billion in grants and loans until 2027, and the provision of humanitarian aid totaling USD 89.99 million to mitigate the impact of the conflict. The EU has also enforced multiple packages of economic and individual sanctions against Russia, demonstrating a firm stance against Russian military intervention. Additionally, efforts to integrate Ukraine into EU structures have been evident through proposals to open accession negotiations and the provision of macro-financial assistance.[5] The military aid to Ukraine amounts to USD 5.42 billion through the European Peace Facility Fund.[6]
However, the deteriorating situation in Ukraine, marked by the apparent collapse of its defenses, underscores the grim reality of a protracted war of attrition. Amidst this backdrop, the proposition of sending weapons and utilizing seized Russian assets to bolster Ukraine’s war effort is met with skepticism.
Such actions have internationalized the conflict and are unlikely to significantly alter the casualty ratio or the strategic outcome of the conflict. Instead, they risk escalating tensions and emboldening Russian military operations, magnifying the potential to exacerbate hostilities, increase the casualty ratio, fueling a vicious cycle of violence and retaliation.
Download Report
Critical Crossroads for EU Foreign Policy Amid Upcoming Elections and Public Dissent
Europe finds itself at a critical juncture, facing challenges that threaten its position.
Moreover, the adverse impact on public sentiment within the EU cannot be understated. Heightened military involvement without clear strategic objectives risks alienating European citizens, further eroding support for such interventionist policies. Therefore, there is palpable skepticism regarding the EU’s efficacy in providing substantial support, with perceptions of a fractured political system hindering cohesive action.
On the other hand, EU’s response to the Israel-Palestine conflict entails a dual approach: providing humanitarian aid to Palestinians while supplying military aid to Israel. Amidst the severe humanitarian crisis in Gaza, EU has allocated an additional USD 73.73 million in humanitarian assistance, bringing the total aid for 2024 to USD 209.26 million.[7] Concurrently, the EU has emerged as a significant supplier of military equipment to Israel, with European countries licensing approximately USD 2.17 billion of military contracts to Israel over the last decade. Despite advocacy from disarmament and peace organizations, European nations continue to provide arms to Israel, including ammunition, drones, and military aircraft components.[8] The significant loss of life within a short timeframe and allegations of genocide has shocked and deeply troubled citizens across the globe, including EU, exacerbating tensions and inflaming public sentiment. This dynamic raises concerns about the EU’s role in perpetuating conflict and supporting the actions of the Israeli government. On an individual state-level however, one can currently see a shift in foreign policy towards this Middle Eastern conflict. Namely, Norway and two EU member-states, Spain and Ireland have recently announced their plans of recognizing the State of Palestine since 28 May 2024.[9]
In conclusion, the current conflicts in EU’s neighborhood disrupted energy supplies, inflated costs, destabilized trade routes, and reduced market confidence of the EU single market. In addition, the double standard approach toward the conflicts triggered criticism for EU’s foreign policy discourse. It also gave rise to far-right sentiment, social discontent, skepticism and controversy among EU citizens regarding their efficacy and ethical implications, which is one of the main reasons for the deepening of the internal divisions within the Union.
02
Socio-Economic Divisions Amid Ongoing Conflicts
02
Socio-Economic Divisions Amid Ongoing Conflicts
EU’s economic prowess is compromised due to the multifaceted challenges stemming from internal socioeconomic disparities, further exacerbated by external conflicts in Eastern Europe and the Middle East. These challenges encompass poverty affecting millions, migration policy reform imperatives due to refugee deaths and criticism regarding human rights violations, youth unemployment, economic uncertainties, digitalization concerns, and climate commitments. Concurrently, the EU contends with rising right-wing movements critical of its principles amidst geopolitical tensions, highlighting the urgent need for collective action in economic and security matters.
Over 140 million people, representing more than 21 percent of the population, are at risk of poverty.[10] EU migration policies face urgent calls for reform, particularly as over 27,000 individuals have lost their lives in the Mediterranean since 2014 while attempting to flee from their war-torn countries.[11] Criticisms regarding human rights violations in the treatment of refugees further compound these concerns.[12][13] Moreover, youth unemployment rates remain alarmingly high in certain EU member-states.[14] Besides the wars in EU’s neighborhood and the Middle East, economic uncertainty, the future stability of the Eurozone, the ramifications of digitalization, as well as issues surrounding data protection and cybersecurity, are prominent concerns among EU citizens. Furthermore, EU lags behind its commitments to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and progress towards energy transition targets. Climate change, renewable energy initiatives, and environmental conservation have emerged as focal issues for voters disillusioned by political rhetoric and unfulfilled promises. All these factors combined have bolstered the rise of right-wing movements, critical or dismissive of EU unity and principles.

However, when it comes to the raging wars in Ukraine and Israel, the societal discontent is evident across EU. In the ongoing EU election campaign, security concerns loom large, particularly for the Baltic States reflecting the complex interplay of geopolitical tensions, socioeconomic challenges, and the imperative for collective European action in defense and security.[15] The current conflict in Ukraine has sparked a range of opinions and feelings across EU nations, leading to notable divisions within societies regarding the ongoing war. At the heart of this polarization is a prevailing sense of doubt about Ukraine’s ability to achieve a decisive victory, with many anticipating a negotiated settlement rather than a clear triumph for either side. This uncertainty influences differing views on how to best support Ukraine, with some advocating for unwavering backing of its territorial integrity while others lean towards encouraging Ukraine to seek a compromise. Furthermore, even traditional allies of Ukraine, like Poland, are experiencing fluctuations in public support, possibly influenced by factors such as trade relations and the challenges of integrating refugees. Such shifts underscore the complexities of maintaining unity among EU member-states in the face of evolving geopolitical dynamics.
Attitudes towards Ukrainian migrants also vary widely across Europe, reflecting broader debates on immigration policy. While some countries express concerns about the potential influx of Ukrainian refugees, others prioritize humanitarian assistance and integration efforts. In addition, worries about the potential ramifications of a re-election of former US President Donald Trump further complicate matters, with fears about its impact on global stability and Ukraine’s prospects of success. Amidst these complexities, there is lingering doubt about the EU’s ability to effectively support Ukraine, with some viewing the EU’s political system as ineffective and favoring a push towards a peace deal. These doubts contribute to divisions among Europeans regarding whether the EU has played a constructive or detrimental role in the Ukrainian conflict, highlighting the diverse perspectives within European societies on this critical issue.
Regarding the events in the Middle East, the European public sentiment show that the Israel-Palestine conflict is perceived as equally impactful. Recent media reports shed light on the widespread protests across Europe, showcasing a spectrum of opinions and reactions to the ongoing conflict. In Brussels, EU employees took to the streets to voice their dissatisfaction with the bloc’s Gaza policy, symbolically mourning the burial of international law, EU agreements, and the UN Genocide Convention.[16] This demonstration highlights a deep-rooted concern among Europeans regarding the perceived erosion of European values in the face of the conflict. Similarly, in Malmo, Sweden, thousands protested against Israel’s participation in the Eurovision final, citing Israel’s conduct in the war on Gaza as grounds for exclusion.[17] This sentiment underscores an anti-war stance among certain segments of European society, who advocate for tangible actions against Israel in response to its actions in Gaza.
Meanwhile, Europe’s response to Israel’s reported preparation for a ground operation in Gaza has been divided, leading to a perceived sense of inaction. While some European countries remain passive, others are grappling with how to respond effectively, showcasing the complexities of forming a unified European stance on the issue.[18] Furthermore, student-led protests across Europe, reflect a growing discontent and desire for action in solidarity with Palestine.[19] Calls for universities to sever ties with Israel and demonstrations against EU research funding for Israel demonstrate a widespread grassroots movement advocating for change in European policies towards the conflict. However, these protests have not been without controversy, as clashes and arrests have occurred during some demonstrations,[20] indicating a rising polarization within European societies regarding the appropriate response to the conflict. This polarization is further exacerbated by Israel’s rejection of a ceasefire agreement, prompting police intervention to disperse pro-Palestine protests at universities across Europe.[21]
Consequently, EU’s economic strength is being increasingly reduced by a complex array of challenges. Internally, the EU grapples with poverty, migration policy reforms and allegations of human rights violations, unemployment, digitalization and climate issues. Externally, the conflicts exacerbate these difficulties by introducing additional economic uncertainties and geopolitical tensions. Simultaneously, the rise of right-wing movements critical of EU principles underscores the urgency for cohesive and collective action in both economic and security domains to safeguard the Union’s stability and future prosperity.
03
Post-Election Foreign Policy Discourse
03
Post-Election Foreign Policy Discourse
The forecast for the upcoming EU elections suggests a continuation of the existing geopolitically-driven foreign policy stances, exerting further pressure on EU’s economic prospects. Such discourse is challenging EU’s economy, bearing the potential to exacerbate already heightened social discontent and catalyze widespread protests throughout Europe. It also increases the probability of war “spilling-over” among EU member-states. The political and public pressure coupled with economic strain will likely be an incentive for the incoming EU parliament to adjust its foreign policy to prioritize EU economy and the well-being of member-states, and work towards peace initiatives in the crisis zones.
EU foreign policy-making is being decided by unanimity among member-states,[22] and the EU has historically encountered challenges due to its intergovernmental nature, allowing each member-state to wield veto power. Despite efforts to formulate common foreign policy strategies, such as the Global Strategy and Strategic Compass, EU foreign policy implementation has lagged behind. Divisions persist between member-states’ interests and EU-level objectives, exacerbating challenges in achieving consensus. This has often led to blocked or diluted common EU positions, hindering effective policy-making and impacting the EU’s international influence and credibility.
These divisions also impact EU’s economy, as EU’s foreign policy is currently focused on external threats which diverts taxpayers’ money to geopolitical conflicts rather than economic prosperity. Protests related to the wars in EU’s neighborhood and against these policies could escalate, especially after the June elections, leading to social unrest and economic instability.
These socio-economic circumstances may deter investment, disrupt economic activities, and shift spending away from essential domestic programs, affecting economic stability. The current EU’s response to international crises has underscored its struggles to act cohesively, raising questions about its geopolitical relevance.
How can we help?
Intelligence Solutions
The combination of business, market and strategic intelligence ensures result-driven outcomes for our customers.
Risk management
Risk management through the responsibility of taking risk ownership while ensuring safety and security
The rise of far-right parties in the EU parliament is expected to further complicate foreign policy dynamics. These parties may exert pressure on mainstream actors, directly blocking consensus-building, aligning with external powers, or resisting the development of EU foreign policy architecture. Consequently, this could impede EU’s ability to agree on policies, degrade policy quality, erode trust among stakeholders, and weaken its international impact. Moreover, the increasing influence of radical right parties in EU politics raises concerns about the erosion of the European project. Their critical stance toward US and EU policies, and prioritization of national interests could disrupt EU cohesion on foreign policy issues like sanctions and military support for Ukraine and Israel. Hungary assuming the EU presidency since July 2024 adds complexity to this landscape, as its political stance may influence EU discussions and decision-making processes. However, the presidency’s role in foreign policy remains limited, with the European Council and the Foreign Affairs Council holding primary responsibility.
Furthermore, the anticipation of a less globally engaged United States under a potential return of Donald Trump to the presidency could prompt anti-establishment and Eurosceptic parties to reject strategic interdependence and international partnerships. This could lead to a more cautious approach to foreign policy decisions, impacting EU unity and its ability to navigate global challenges effectively.
Therefore, the outlook for the forthcoming EU elections indicates that geopolitically-driven foreign policy stances will persist, further straining the EU’s economic prospects. This ongoing discourse not only challenges the economy but also risks intensifying social discontent and sparking widespread protests across Europe, as well as increasing the likelihood of spilling the war over to certain EU countries. Consequently, the political and economic pressure will likely prompt the incoming EU parliament to prioritize economic stability and the well-being of member-states, as well as to advance peace initiatives in the conflict regions.