Listen to the article – The War’s Shadow Over Israel’s Pillar of Progress
Israel’s technological sector is experiencing difficulties as a result of series of unfavorable events in the past period. The October 7 attacks have shocked Israeli economy disrupting the technological sector, creating short-term opportunities, however, it also led to increased security concerns, political instability, and economic challenges that threaten its resilience and growth in the long-term.
Israel’s technology sector which is recognized as one of the most advanced globally, stands as the most productive segment of the nation’s economy. It has been instrumental as an economic engine for Israel, providing resilience during economic downturns and enabling swift recoveries. Employing approximately 12 percent of the national workforce, it contributes 20 percent to the gross domestic product and accounts for over half of the country’s exports.[1] The seamless connection to the global economy, created opportunities for investment and Israel’s R&D sector currently relies on foreign investments, with contributions reaching as high as fifty percent.[2] Therefore, Israel’s pillar of progress is one of the most important aspects of the country’s economic well-being.
With the world’s second-largest cybersecurity cluster, comprising over 470 startups and substantial R&D operations from multinational giants like Google, Microsoft, Apple, and Intel, Israel has cemented its position as a key player in the global cyber landscape.[3] The International Institute for Strategic Studies report of 2021 acknowledged Israel as one of the strongest global cyber powers, highlighting the nation’s strategic investments and successes in cyberspace. In 2022, Israel’s revenues solely from the technological sector amounted to USD 71 billion, out of which 10.5 percent are attributable to foreign investments.[4] However, Israeli high-tech sector experienced a significant downturn in 2023, assigned to both global economic trends and specific local political and security challenges.
How can we help?
Intelligence Solutions
The combination of business, market and strategic intelligence ensures result-driven outcomes for our customers.
Risk management
Risk management through the responsibility of taking risk ownership while ensuring safety and security
Even though six hundred start-up companies were founded and USD eight billion raised by technological companies in 2023, it nevertheless is a 60 percent decrease in comparison to the previous year.[5] Investment levels have plummeted to figures reminiscent of 2018, with a notable reduction in the number of fundraising rounds and early-stage investments.
Moreover, the judicial reforms pursued by the Israeli government in July 2023, aimed at reducing the powers of the Supreme Court, have ignited widespread protests and raised significant concerns among investors and analysts. This political turmoil has contributed to the decline of the shekel and stock market’s underperformance, casting a shadow over foreign investments that were previously robust. There is growing apprehension that these reforms could destabilize the investment climate in Israel’s critical technology sector, potentially affecting the overall economic landscape and the country’s credit rating.[6] Compounding these concerns, in August 2023, there was a notable trend of Israeli technological startups incorporating in the United States. This shift is driven by favorable business conditions in the US and uncertainties surrounding Israel’s legal and tax environment. While these judicial reforms do not directly impact the technological sector, the perceived instability has prompted entrepreneurs to seek more stable environments abroad.
If this was not enough, the situation deteriorated further with the October 7 attacks, fracturing Israel’s enduring sense of security. Besides causing a solid financial shock to the current administration, it has also created uncertainties for the country’s long-term economic prospects. And war, by its very nature, disrupts life, businesses, and society, yet prolonged warfare translates to greater military-related expenditures that exact a toll on broader societal and economic matters. Also, the current war bears a potential for regionalization bearing in mind the current geopolitical shift. This complex set of circumstances will likely present substantial challenges to the country’s pillar of progress, raising concerns about its future resilience and growth. Nevertheless, according to the OECD’s 2024 economic outlook, Israel’s economy is projected to grow by 1.9 percent in 2024 and 4.6 percent in 2025, suggesting an initial recovery from the October 7 attacks. Even so, the risks remain elevated, potentially deterring both internal and foreign investments and slowing the growth of Israel’s technological ecosystem until economic confidence is restored.
The analysis aims to inform investors of the multifaceted opportunities and challenges currently impacting Israel’s technological sector during this round of hostilities in Gaza and amid the present geopolitical shifts, arguing that Israel’s technological sector will deteriorate further should the current conflict endures. Despite its historical resilience, government’s support and the immediate demand in defensive technologies, the ongoing conflict introduced considerable security issues that disrupted operations and deterred foreign investment. The current geopolitical shift exacerbates these challenges, undermining investors’ confidence in the sector’s future stability. Market volatility, coupled with labor and funding shortages, further constrains the sector’s innovation and growth prospects. In the mid-term, these factors are likely to further impede progress and reduce the sector’s competitiveness. Prolonged conflict, however, would only intensify these issues, potentially crippling a cornerstone of Israel’s economic and technological advancement.(Fig.1)
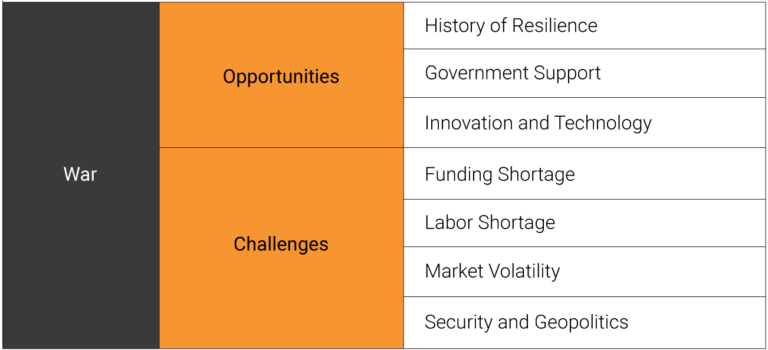
Figure 1. Opportunities and challenges for Israel’s technological sector